Raised bed gardening offers a multitude of advantages over traditional in-ground gardening, making it an attractive choice for gardeners of all levels, especially those preparing for survival situations. By elevating the planting area, raised beds provide a controlled environment that optimizes growing conditions, increases yields, and simplifies maintenance.
Table of Contents
What is Raised Bed Gardening?
Raised bed gardening involves creating an elevated planting area, typically enclosed by a frame made of wood, stone, or other materials.
The beds are filled with a carefully prepared soil mix, creating a separate, contained growing space above the existing ground level.
This method contrasts with traditional in-ground gardening, where plants are grown directly in the native soil.
For those interested in urban survival gardening or homesteading in an apartment, raised beds can be a valuable solution.
Here are the 10 life-changing benefits of raised bed gardening listed in the article:
- Improved Drainage
- Improved Soil Quality
- Increased Accessibility
- Convenience
- Extended Growing Season
- Higher Yields and Productivity
- Pest and Disease Control
- Efficient Use of Space
- Aesthetic Appeal and Organization
- Cost and Maintenance Considerations
Improved Drainage and Soil Quality

One of the primary benefits of raised bed gardening is the improved drainage and soil quality it offers.
Better Drainage
Raised beds allow excess water to drain more efficiently, preventing waterlogging and root rot. This is particularly advantageous in areas with heavy clay soils or poor drainage conditions.
Customizable Soil Mix
Gardeners have complete control over the soil composition in raised beds. By creating a custom soil mix tailored to the specific needs of the plants, gardeners can ensure optimal growing conditions. This mix can include amendments such as compost, peat moss, or vermiculite, providing the ideal balance of nutrients, water retention, and aeration. For tips on healthy garden soil and soil hacks for gardening, check out these resources.
Reduced Soil Compaction
Raised beds minimize soil compaction, as the planting area is not walked on or subjected to heavy foot traffic. Loose, well-aerated soil promotes healthy root growth and better nutrient uptake.
| Soil Quality Factor | Raised Bed | In-Ground Garden |
|---|---|---|
| Drainage | Excellent | Varies |
| Customization | High | Low |
| Compaction | Minimal | Moderate to High |
Increased Accessibility and Convenience
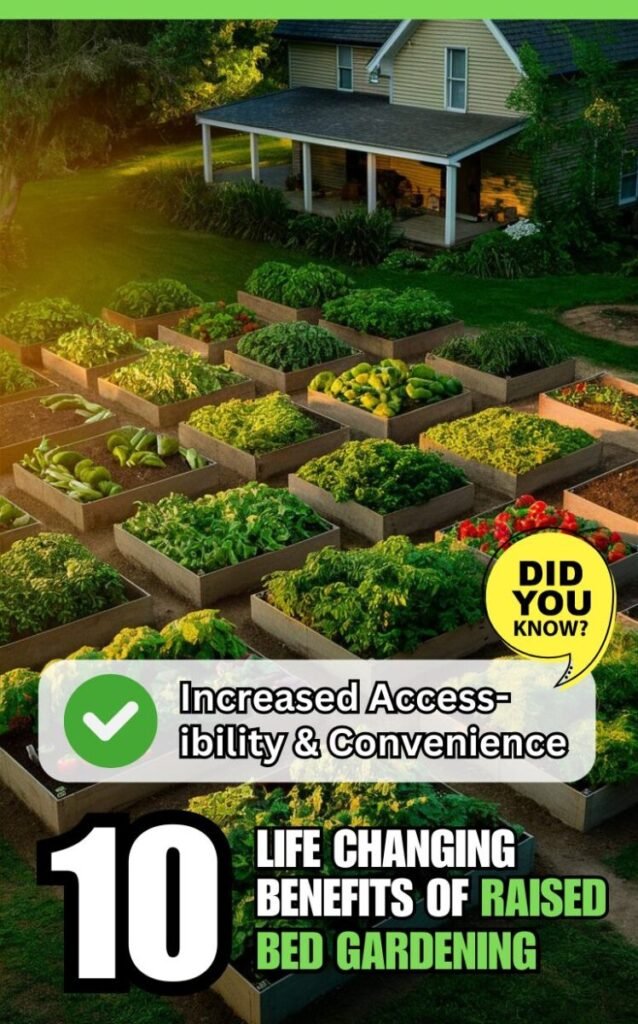
Raised beds offer gardeners increased accessibility and convenience, making gardening more enjoyable and less physically demanding.
- Easier on the Back: With raised beds, gardeners don’t have to bend over as much, reducing strain on the back and knees.
- Wheelchair and Senior-Friendly: The elevated planting surface makes raised beds more accessible for those with mobility challenges or disabilities.
- Better Weed Control: Raised beds create a physical barrier against weeds, reducing the need for constant weeding and minimizing the spread of invasive plants from surrounding areas.
Extended Growing Season

Raised beds can extend the growing season, allowing gardeners to start planting earlier in the spring and continue harvesting later into the fall. For those looking to maximize their growing potential, check out our guide on winter gardening techniques.
- Faster Soil Warming: The elevated nature of raised beds allows the soil to warm up more quickly in the spring, enabling earlier planting and germination.
- Better Frost Protection: Raised beds can be covered with row covers, cloches, or cold frames to protect plants from late spring or early fall frosts, prolonging the growing season.
- Season Extension Techniques: Gardeners can employ techniques like succession planting, interplanting, and crop rotation to maximize the productivity of their raised beds throughout the extended growing season.
Higher Yields and Productivity

Raised bed gardening often results in higher yields and increased productivity compared to traditional in-ground gardens.
- Intensive Planting: Raised beds allow for closer spacing of plants, maximizing the use of available space and increasing the overall yield per square foot. For small-space gardening ideas, check out our guide on vegetables for small-space gardening.
- Optimized Root Zone: The contained environment of raised beds creates an optimal root zone, promoting healthy root growth and better nutrient absorption.
- Better Nutrient Retention: The raised bed’s soil mix retains nutrients more effectively, reducing the need for frequent fertilization and ensuring consistent plant growth. You can also explore household items for garden fertilizers as a cost-effective option.
- Crop Rotation Benefits: Crop rotation is easier in raised beds, helping to prevent soil-borne diseases, pests, and nutrient depletion, leading to higher overall productivity.
Pest and Disease Control

Raised beds can provide natural pest and disease control benefits, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
- Physical Barrier: The raised bed structure creates a physical barrier, deterring pests like rabbits, voles, and gophers from accessing the plants.
- Better Air Circulation: The elevated planting area promotes better air circulation, reducing the risk of fungal diseases and other moisture-related problems.
- Crop Rotation for Pest Management: Crop rotation in raised beds can help disrupt pest life cycles and prevent the buildup of soil-borne pathogens. Additionally, you can explore natural pest killers and plants that repel pests for eco-friendly pest control solutions.
Efficient Use of Space

Raised bed gardening allows for efficient use of available space, making it an ideal choice for urban or small-scale gardening.
- Small Footprint, High Output: Raised beds maximize productivity in a smaller area, producing a high yield from a concentrated space. Check out our guide on high-yield vegetables for optimal crop choices.
- Vertical Gardening Options: Raised beds can be combined with vertical gardening techniques like trellising or caging, further increasing the yield per square foot. Explore our list of best plants for vertical gardening for inspiration.
- Interplanting and Companion Planting: The contained nature of raised beds facilitates interplanting and companion planting, allowing for the efficient use of space while promoting beneficial plant interactions.
Aesthetic Appeal and Organization
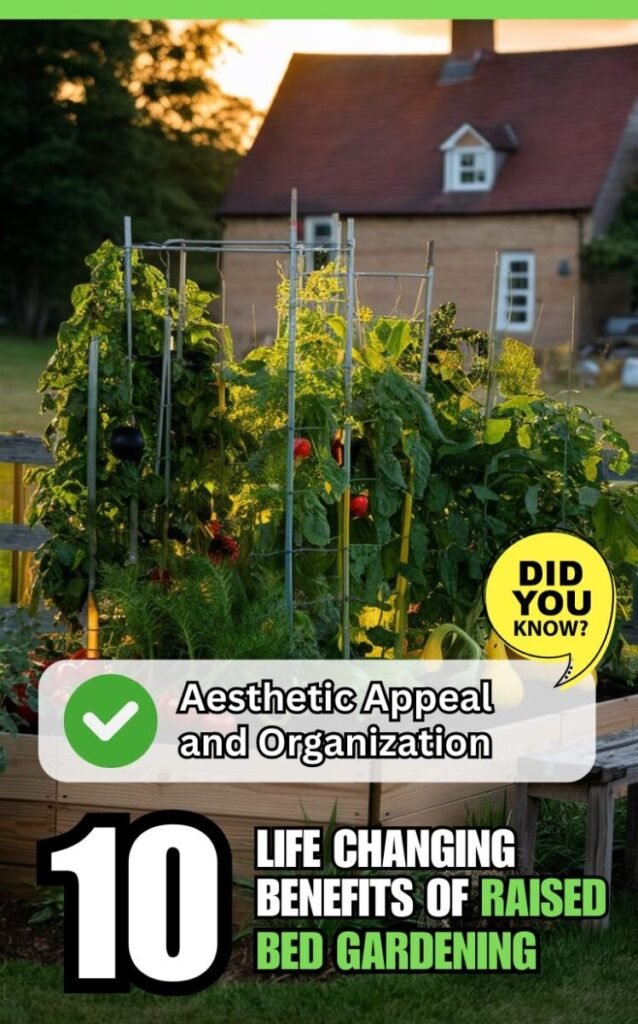
In addition to their practical benefits, raised beds can enhance the aesthetic appeal and organization of your garden.
- Neat and Tidy Appearance: Raised beds create a well-defined and tidy appearance, adding structure and visual interest to your garden.
- Garden Design Flexibility: Raised beds can be incorporated into various garden designs, from formal layouts to informal, naturalistic settings, allowing for creative expression.
- Raised Bed Customization: Gardeners can customize the size, shape, and materials used in their raised beds, creating unique and personalized garden features that complement their overall landscape design.
Cost and Maintenance Considerations

While raised bed gardening offers numerous advantages, it’s important to consider the associated costs and maintenance requirements.
- Initial Investment: Building raised beds requires an upfront investment in materials and labor, which can vary depending on the size and complexity of the project.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Raised beds require regular maintenance, such as replenishing the soil mix, monitoring moisture levels, and repairing or replacing any damaged components over time.
- Long-Term Durability: Choosing high-quality, weather-resistant materials for your raised bed construction can ensure longevity and reduced maintenance costs in the long run.
Getting Started with Raised Bed Gardening

If you’re interested in incorporating raised bed gardening into your survival preparedness plans, here are some steps to get started:
- Planning and Site Selection: Determine the ideal location for your raised beds, considering factors like sunlight exposure, proximity to water sources, and accessibility.
- Materials and Construction: Choose the materials for your raised bed frame based on your budget, desired aesthetics, and durability requirements. Common options include wood, stone, or composite materials. For a comprehensive guide, check out our container gardening guide.
- Filling and Soil Preparation: Fill your raised beds with a carefully prepared soil mix tailored to the plants you plan to grow. Consider adding compost, aged manure, or other amendments to enhance soil fertility and structure. Explore our guide on the perfect compost pile for tips on creating nutrient-rich compost.
By embracing raised bed gardening, you can enjoy a more productive, accessible, and organized gardening experience while maximizing your yields and minimizing the challenges associated with traditional in-ground gardening. With proper planning and maintenance, raised beds can be a valuable asset in your survival preparedness efforts, providing a reliable source of fresh produce and ensuring food security in times of need.
For those interested in growing food in unconventional spaces, check out our resources on:
You can also explore:
For space-saving gardening ideas.
If you’re new to gardening, our guides on:
Can help you get started on the right foot.
For those interested in maximizing their survival crop yields, check out our resources on:
- High-calorie crops in containers
- Highest-calorie survival crops
- Calorie-dense survival crops
- Crucial food for survival
We also have guides on specific survival crops, such as:
To help you plan your survival garden.
For those interested in expanding their gardening knowledge, our articles on:
Can provide valuable insights.
Lastly, we have resources on more advanced topics:


